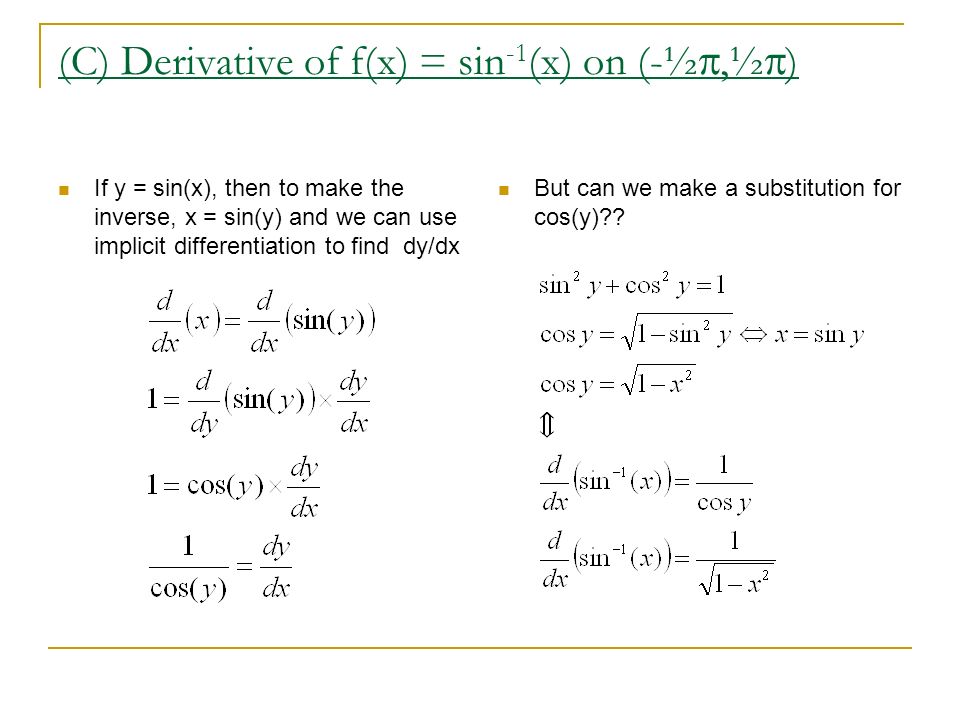
Y = d d x ( sin x × log e x) In this differentiation problem, the variable y represents a function in x Hence, it can be differentiated with respect to x and do not think that y is a constant Therefore, the function y can be differentiated by the derivative rule of logarithms 1 y × d y d x = d d x ( sin 1 Answer to Verify that y = 3 sin 2x is a solution of d 2 y dx 2 4y = 0 Verify that 3 ex , Ax e x , Ax e x B e x , where A, B are constants, all satisfy the differential equation d 2 y dx 2 −Find Dy/Dx for Y = Sec^(1) (1/(2x^2 1)), 0 < X < 1/Sqrt2

Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Find Dy Dxif Dy Dx 2cos 1xthis Is Class 12 The Problem Plz Help Brainly In
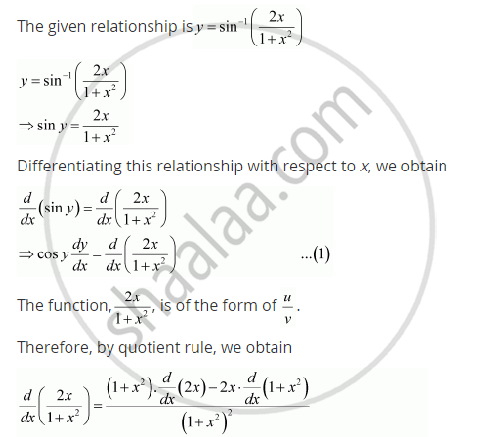
Y=sin^-1(2x/1+x^2) find dy/dx
Y=sin^-1(2x/1+x^2) find dy/dx-1 Consider the curve y=x^2 a write down (dy)/(dx) My answer 2x The point P(3,9) lies on the curve y=x^2 b Find the gradient of the tangent to the curve at P My answer 2*3=6 c Find the equation of the normal to the curve Math Sinh 2x=8 coshx You can view more similar questions or ask a new questionY Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Find Dy Dx;Find Dy Dx If Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 hviezdoslavov kubín 7 ročník hugolin gavlovic valaska skola mravov stodola if f x x 3 x 2 x 1 then f 2 humanizmus a renesancia znaky ii rákóczi ferenc portr4) We want to find dy/dx, which is on the LHS To get this dy/dx on its own we can multiply both sides by y So we get dy/dx = y log(2) 5) To finish this question we need to sub




Ex 2 2 13 Inverse Trigonometry Tan 1 2 Sin 1 2x 1 X2
Points 5 years ago Given eqn xe^ (xy) – y = sin^2x, Differentiate y wrt x as (1)e^ (xy) xe^ (xy)* 1y xdy/dx – dy/dx = sin2x collect dy/dx, put x = 0 dy/dx = 1Start your free trial In partnership with You are being redirected to Course Hero I want to submit the same problem to Course Hero CancelFind dy/dx y=sin (x)^2 y = sin2 (x) y = sin 2 ( x) Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (sin2(x)) d d x ( y) = d d x ( sin 2 ( x)) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d d x
View QUESTION BANK ENG MATHS Ipdf from MATH MA6151 at Rajalakshmi Engineering College QUESTION BANK PART A 1Find dy dx x if y = x 2Find ,If an equation implicitly defines y as a function of x, there is a way to find dy/dx without first explicitly finding y as a function of x, called implicit differentiation We will use the equation y x 2 1 = 0 to illustrate this technique Instead of explicitly solving for y, assume that it would be possible to solve for y in terms of x; differntiate wrt x If y = sec1 ( x 1/ x – 1) sin1 ( x – 1 / x 1), show that dy/dx = 0 Queries asked on Sunday & after 7pm from Monday to Saturday will be answered after 12pm the next working day
View TUTORIAL 4pdf from MATH EQT101 at University of Malaysia, Perlis TUTORIAL 4 Question 1 Find dy dx a) y 5e 3 x 4 ln 3x d) y ln x 4 3 cos 2 x 5 x3 c) y 2 cot 3x 6 x 5 e) y ln b) y 7 sin 4 xSolved Find dy/dx By implicit differentiation 2x^2 xy Cheggcom Math Calculus Calculus questions and answers Find dy/dx By implicit differentiation 2x^2 xy y^2 = 2 x^3 xy^2 y^3 = 1 xe^y = x y cos (xy) = 1 sin y e^y sin x = x xy xy = Squareroot x^2 y^2 x sin y y sin x = 1Bernoulli's equation has form, \frac{dy}{dx}p(x)y=q(x)y^n Now, consider this, \frac{dz}{dx}z^2x=z^2z This easily simplifies to, \frac{dz}{dx}z=(1x^2)z^2 where p(x)=1 Find bounded solutions of this ODE




If Y Sin 1 2x1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 21 X 2 Show That Dydx 4 1 X 2




Ex 2 2 13 Inverse Trigonometry Tan 1 2 Sin 1 2x 1 X2
Y' = dy/dx = sin x 1/2( sin 2x)(2) ⇒ y' = sin x – sin 2x y' = 0 ⇒ sin x – sin 2x = 0 ⇒ sin x – 2 sin x cos x = 0 ⇒ sin x (1 2 cos x) = 0 ⇒ sin x = 0 or 1 2 cos x = 0 ⇒ sin x = 0 or cos x = 1/2 ⇒ x = 0 or x = 2π/3 These are the possible points of Local maximum and Local Minimum y'' = I'll let you do this one In general, Mistype in 2 is just By the way, I don't see anything gained by taking the logarithm in the first problem you posted It is just as easy to differentiate both sides of e 2x = sin (x 3y) the way it stands 2eFind dydxif, y = 3x1(2x 3)(5x)23



B1 6 Derivatives Of Inverse Trig Functions Ppt Download




If Y Sin 2tan 1 1 X 1 X 1 2 Then Find Dy Dx And If 5 X 5 Y 5 X Y Then Prove That Dy Dx 5 Y X 0 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Q011rcnn
Ex 53, 13 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 in, y = cos–1 (2𝑥/( 1 𝑥2 )) , −1 < x < 1 𝑦 = cos–1 (2𝑥/( 1 𝑥2 )) Let 𝑥 = tan𝜃 𝑦 = cos–1 ((2 tan𝜃)/( 1 𝑡𝑎𝑛2𝜃 )) 𝑦 = cos–1 (sin 2θ) 𝑦 ="cos–1" (〖cos 〗(𝜋/2 −2𝜃) ) 𝑦 = 𝜋/2 − 2𝜃 Putting value of θ = tan−1 x 𝑦 = 𝜋/2 − 2 〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^(−1) 𝑥 Si I will just put K equal 1 here and y equals x 3 2x K and put it down here So I am finished This is the answer This is the function y = x 3 2x 1 Its derivative is 3x 2 2 And it passes through the point (1,4) And now for the graph of the function, We can see that it passes through (1,4) We were given the `dy/dx` expression and we have found the "y = " expressionSolution Given y = sin x e x dy/dx = cos x e x dx/dy = 1/ (cos x e x) d 2 x/dy 2 = (cos x e x )0 – (sin x e x )dx/dy / (cos x e x) 2 = (sin x – e x) / (cos x e x ) (cos x e x) 2 = (sin x – e x )/ (cos x e x) 3 Hence option (1) is the answer Was this answer helpful?




Solved Assignment 1 If Y Xsinx Find Dx Dy 2 If Y Chegg Com



Solved 1 For 1 12 Find Dy Dx For 1 Y Xe 3x 2 Y Chegg Com
If y = sin−1 x, then sin y = x,−π/2 ≤ y ≤ π/2 Therefore, to find y = sin−1(−3/22, we must find an angle y whose sine is 3/2 There are many possible angles with this sine, but the range of y = sin−1 x is Alg2/Trig Find the exact value of the trigonometric function given that sin u = 5/13 and cos v = 3/5Multiply by 2 to get y 2 = x 2 2x 16 Finally take a square root to obtain Example Find the equation of the function that has the following properties Slope = y sin x and passes through the point (0,2) Solution Since the slope is the derivative, we have dy / dx = y sin x Separating gives dy = sin x dx y Integrating both sides givesSolution Solution y = sin − 1 (1 x 2 2 x ) ⇒ sin y = 1 x 2 2 x ⇒ cos y = 1 − sin 2 y = 1 − (1 x 2 2 x ) 2 = 1 x 2 1 − x 2 Differentiating it wrt x, cos y d x d y = (1 x 2) 2 2 (1 x 2) − 2 x (2 x) ⇒ cos y d x d y = (1 x 2) 2 2 (1 − x 2) ⇒ d x d y = cos y 1 ((1 x 2) 2 2 (1 − x 2) ) ⇒ d x d y = 1 − x 2 1 x 2 ∗ ((1 x 2) 2 2 (1 − x 2) ) ⇒ d x d y = 1 x 2 2



Find Dy Dx Of The Following I Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Ii Y Tan 1 3x X 3 1 3x 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Cos 1 2x 1 X 2 Then Find Dydx
(dy)/(dx)=2/sqrt(14x^2) We can use here the formula for derivative of sin^(1)x, which is d/(dx)sin^(1)x=1/sqrt(1x^2) As such to find derivative (dy)/(dx) for y=sin^(1)2x using chain rule is given by (dy)/(dx)=1/sqrt(1(2x)^2)xxd/(dx)(2x) = 2/sqrt(14x^2)Given y=sin −1( 14 x2 x1 )=sin −1( 1(2 x) 22×2 x )Let 2 x=tanθ θ=tan −1(2 x)So y=sin −1( 1tan 2θ2tanθ )=sin −1(sin2θ)=2θ=2tan −1(2 x)Differentiating on both sidesdxdy = 1(2 x) 22 ×2Learn how to solve differential equations problems step by step online Solve the differential equation dy/dx=(2x)/(3y^2) Take \\frac{2}{3} out of the fraction Rewrite the differential equation in the standard form M(x,y)dxN(x,y)dy=0 The differential equation y^2dy\\frac{2}{3}xdx=0 is exact, since it is written in the standard form M(x,y)dxN(x,y)dy=0, where M(x,y) and N(x,y) are




Differentiate Y Sin 1 X2 Root 1 X2 X Root 1 X4 Maths Meritnation Com




Find Dy Dx If Y Sin 1 X Sin 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 0 X 1 Mathematics Shaalaa Com
if y = (1 sin2x/1 sin 2x) 1/2 show that dy/dx sec 2 (π/4 – x) = 0 donot go shortcut if y = log tan (∏/4 x/2) show that dy/dx = sec x donot go shortcut if y = log (x (1 x 2 ) 1/2 ) prove that dy/dx = 1/log(x (1 x 2 ) 1/2 ) 1/(1 x 2 ) 1/2Calculation ( 1 − x 1 x) Let x = tan 2 z z) = cos 1 (cos 2z) = 2z z) = 1 x ( 1 x) Ace your Mathematics and Differential Calculus preparations for Evaluation of derivatives with us and master Trigonometric Function for your exams Learn today!So,the 'y' in the question,arcsin (2x/1x^2) is a little difficult to handle,so a smart substitution has been done in the form of x=tanθ which simplifies the 'y' to be equal to 2 arctan (x) Now,y=2tan^1 (x) Differentiating both sides,we get dy/dx=2*1/1x^2 as derivative of tan^1 (x) is 1/1x^2 And dy/dx is what was asked in the question



If Y Sin 1 X 2 Then Prove That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx 2 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Sin 1 5x 12 1 X 2 1 2 13 Find Dy Dx Mathematics Topperlearning Com Otpu9qyy
If y = x2 sin 1/x then dy/dx = ?KCET 15 If y= log ( (1x2/1x2)) then (dy/dx) is equal to (A) (4x/1x4) (B) (4x3/1x4) (1/4x4) (D) (4x3/1x4) Check Answer and Solut1 x = sin(xy^2), Find dy/dx by implicit differentiation



1



If Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 0ltxlt1 Prove That Dy Dx 4 1 X 2 B X 1
The answer given in the book $\sec x =y(\tan x c)$ Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Get an answer for '`x sin(y) y sin(x) = 1` Find `(dy/dx)` by implicit differentiation' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesCall the resulting function y(x) for simplicity



Differentiate Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 With Respect To Cos 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 If 0 X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Find Dy Dx For Y Sin 1 2xsqrt 1 X 2 1 Sqrt2 X 1 Sqrt2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com
2 dy dx y = 0If Sin 2theta Plus Sin 2phi 1 2 And Cos 2theta Plus Cos 2 Phi 3 2 Then If Sin 4 A A Plus Cos 4 A B 1 A Plus B Then The Value Of If sin A sin B sin C = 3 4 5, then cos A cos B is equal toFind dy/dx of y=cos^1 (2x)*sin^1 (2x) Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Who are the experts?




If Y Sin 2sin 1 X Then Dy Dx Youtube




Find Dy Dx In The Following Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2
Transcript Ex 53, 9 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 in, y = sin^(−1) (2𝑥/( 1 2𝑥2 )) 𝑦 = sin^(−1) (2𝑥/( 1 2𝑥2 )) Putting x = tan θ 𝑦 = sin^(−1Find dy/dx of ,y=1/sin(2x/1x^2) Ask questions, doubts, problems and we will help you Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange




Example 3 Show That Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 2 Sin 1 X Class 12



1
Move 2 2 to the left of cos ( 2 x) cos ( 2 x) Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that d d x x n d d x x n is n x n − 1 n x n 1 where n = 1 n = 1 Multiply 2 2 by 1 1 Reform the equation by setting the left side equal to the right side Replace y' y ′ with dy dx d y d xY*sin(x^2) = xsin(y^2), Find dy/dx by implicit differentiationMost Used Actions \mathrm {implicit\derivative} \mathrm {tangent} \mathrm {volume} \mathrm {laplace} \mathrm {fourier} See All area asymptotes critical points derivative domain eigenvalues eigenvectors expand extreme points factor implicit derivative inflection points intercepts inverse laplace inverse laplace partial fractions range slope




Ex 5 4 2 Differentiate E Sin 1 X Teachoo Ex 5 4




Ex 5 3 14 Find Dy Dx In Y Sin 1 2x Root 1 X2 Cbse
Our online expert tutors can answer this problem Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!KEAM 11 If y= sin 2 cot 1√(1x/1x), then (dy/dx) is equal to (A) 2 sin 2x (B) sin 2x (1/2) (D) (1/2) (E) cos 2x Check AnsExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high 100% (2 ratings) Transcribed image text Question 7 Find dy of y COS 1 (2a) sin 1 (2a) Previous
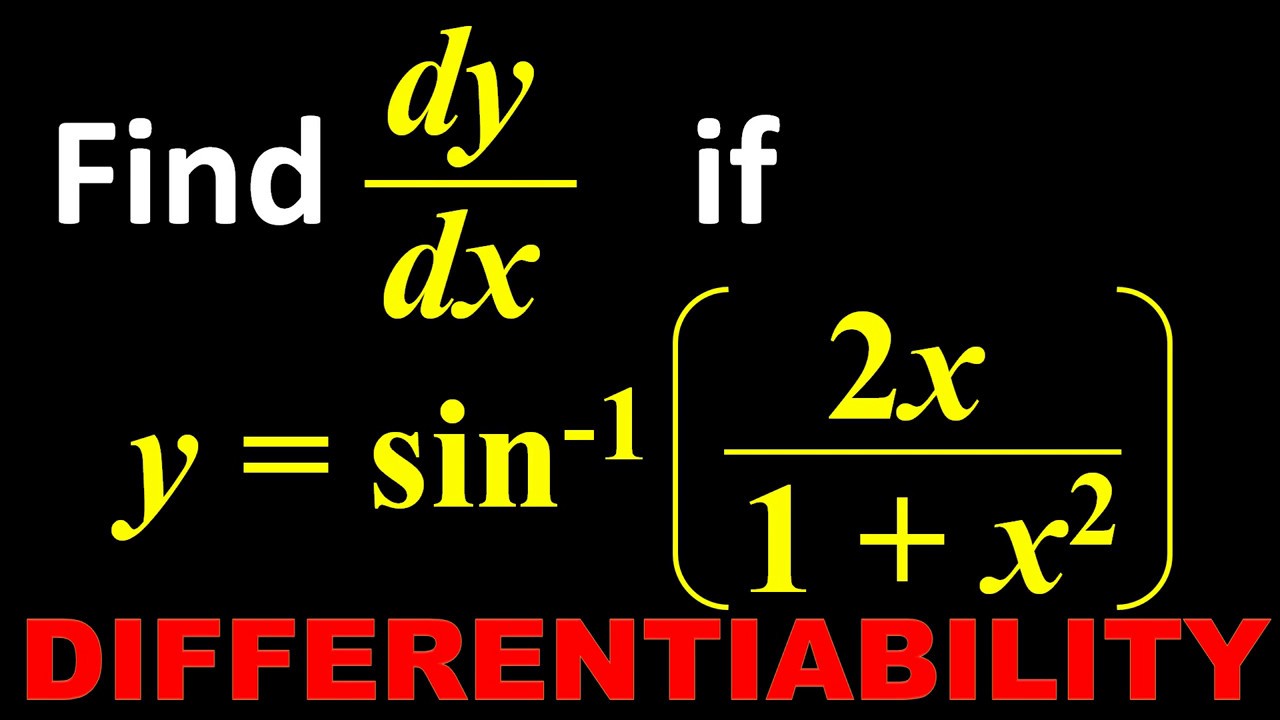



10 Derivative Find Dy By Dx Of Y Sin 1 2x Upon 1 X2 Youtube
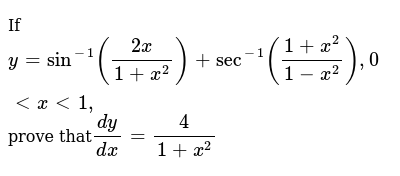



If Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 0ltxlt1 Prove That Dy Dx 4 1 X 2 B X 1
A x sin 1/x cos 1/x B cos 1/x 2x sin 1/x C x sin 1/x cos 1/x D None of theseLet's simplify it First dy/dx = (y/x 1)/(y/x 1) Taking y = vx dy/dx = v xdv/dx Therefore, dx/x = (v 1)dv / (v^2 1) Integrating we get log (1/x) logc = arctan (y/x) 1/2 logTherefore , dt/dx = 1/2*(d/dx)(1cos2x) Or , dt/dx = 1/2*(2)(sin2x) = 1/2*(2sin2x) , Or , dt/dx = sin2x Differentiating cos2x wrt x , we get (sin2x)*2 using chain rule 2 Continue Reading



Find Dy Dx At X 1 When Sin Y Sin Pi X 2 3 2 Sec 1 2x 2 X Tan Ln X 2 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



1
If y = sin^1 (x√(1 x) √x √(1 x^2) and dy/dx = 1/2 √x√(1x^2) p, then p is equal to asked in Mathematics by ShivamK ( 6k points) jee
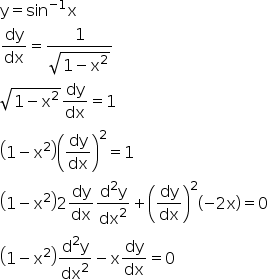



If Y Sin 1 X Prove That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 X Dy Dx 0 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Psl1owbb



If Y Sin 2 Sin 1 X Show That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx 4y Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Differentiate Tan 1 1 X2 1 2 1 X Wrt Sin 1 2x 1 X2 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Yx862gdd




Ex 5 3 12 Find Dy Dx In Y Sin 1 1 X2 1 X2 Chapter 5
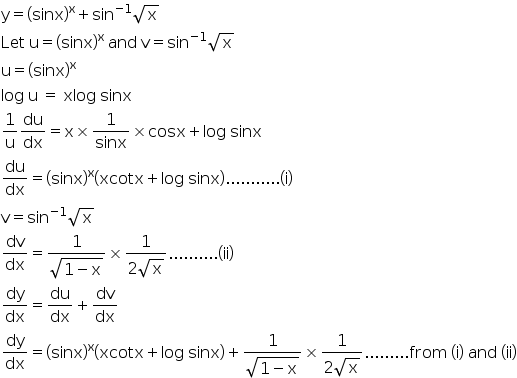



If Y Sinx X Sin 1 X 1 2 Find Dy Dx Explain In Great Detail Do Not Go Shortcut Mathematics Topperlearning Com W0t3auii



If Y Sin A Sin 1 X How Do You Prove That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx A 2y Quora




Ex 7 6 22 Integrate Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Teachoo Ex 7 6



How To Solve This Problem 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 1 X Dy Dx Y Sin 2log 1 X Quora



Find Dy Dx In The Following Y Sin 1 2xsqrt 1 X 2 1 Sqrt 2 Lt X Lt 1 Sqrt 2



Find Dy Dx When X Cos 1 1 1 T 2 And Y Sin 1 1 1 T 2 T R Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
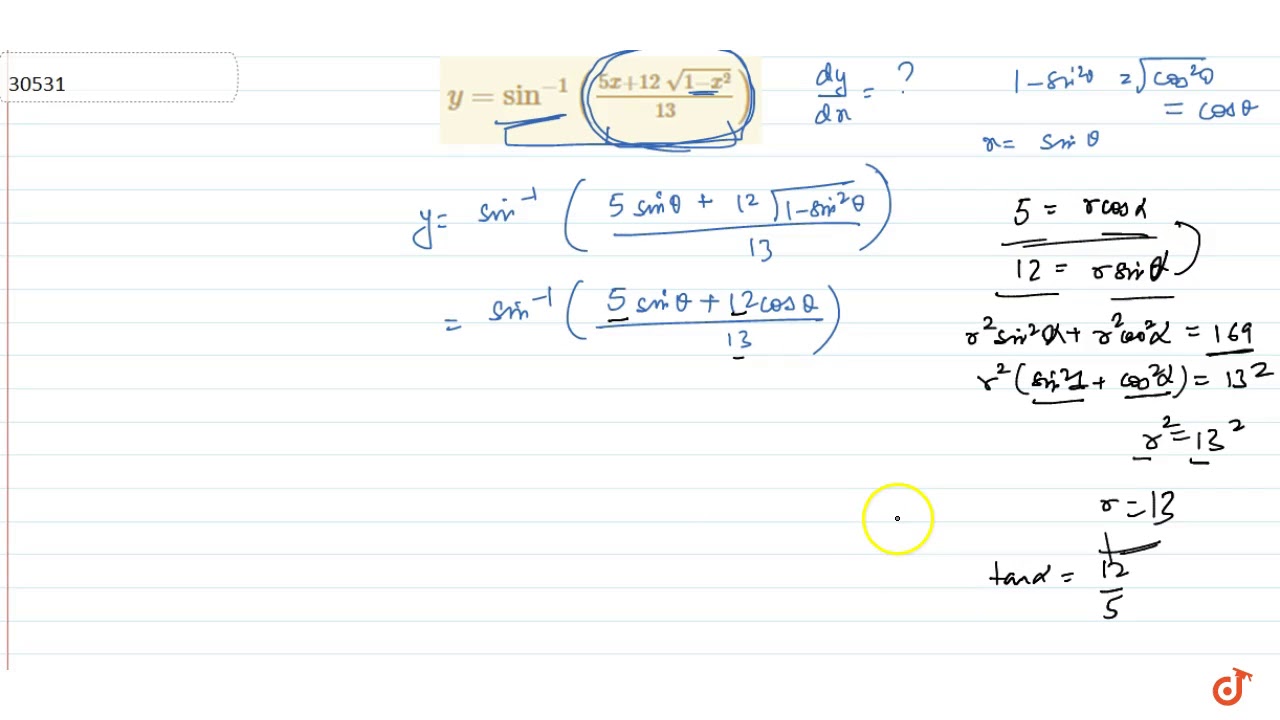



Y Sin 1 5x 12sqrt 1 X 2 13 Youtube



If Y Cos 1 2x 3 1 X 2 13 Then Find Dy Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Find Dy Dx In The Following Y Sin 1 2x Sqrt 1 X 2 1 Sqrt 2 Lt X Lt 1 Sqrt 2




If Y Sin Inverse 5x 12 Root 1 X2 By 13 Find Dy By Dx Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




Ex 5 3 9 Find Dy Dx In Y Sin 1 2x 1 2x2 Chapter 5




Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Find Dy Dxif Dy Dx 2cos 1xthis Is Class 12 The Problem Plz Help Brainly In



Differentiate The Following With Respect To X Sin 1 2 X 1 3 X 1 36 X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Q36 If Y Sin 1 5x 12 1 X 2 13 Find Dy Dx Youtube



If Y Log Cos X Sin X Log Sin X Cos X 1 Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Find Dy Dx At X P 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




What Is The Differentiation Of Sin Inverse X Sin 1 X Teachoo




If Y Sin 1 X 1 X2 1 2 Show That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 3x Dy Dx Y 0 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Wa3tv55
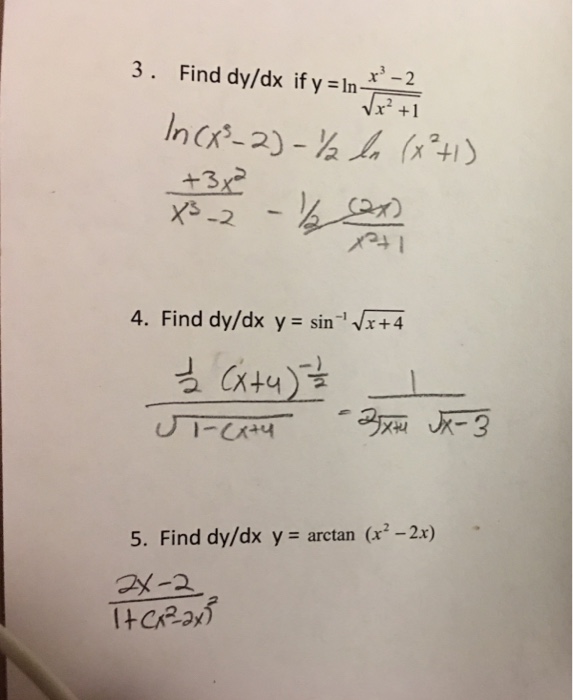



Solved Find Dy Dx If Y Ln X 3 2 Squareroot X 2 1 Find Chegg Com
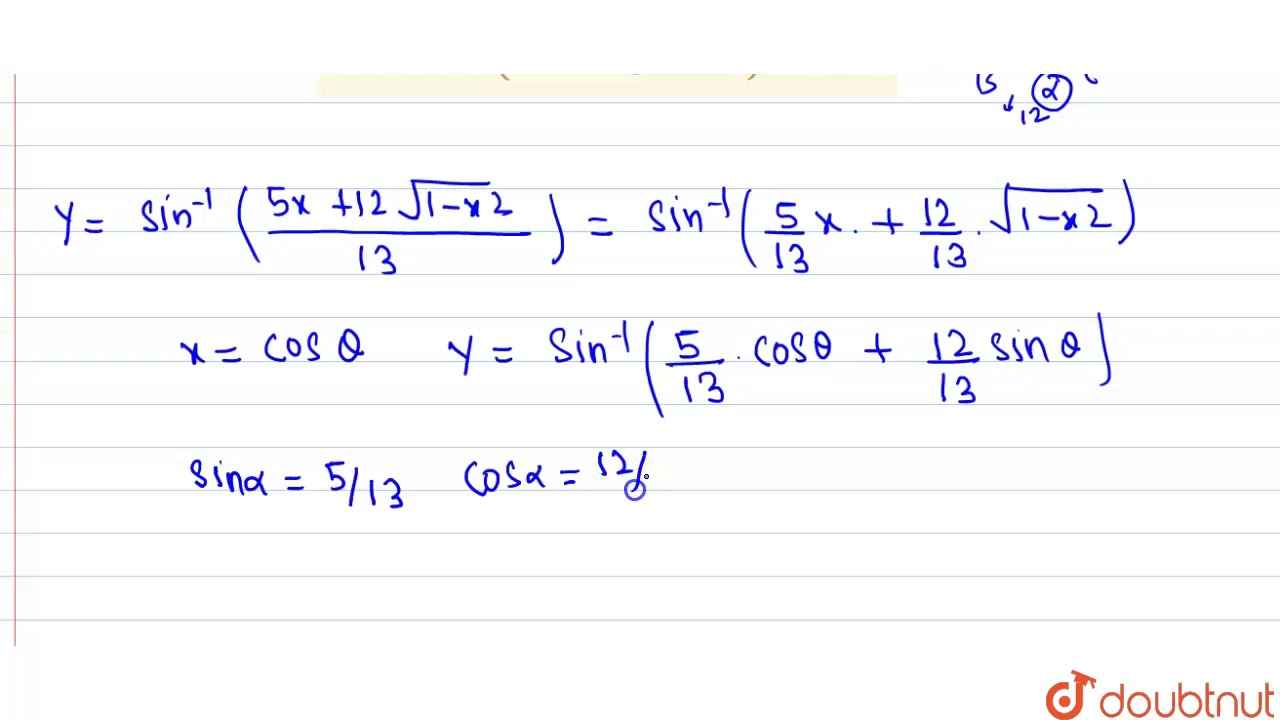



If Y Sin 1 5x 12 Sqrt 1 X 2 13 Find Dy Dx Youtube



Find Dy Dx For Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Example 41 If Y Sin 1 X Show That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 X Dy Dx 0
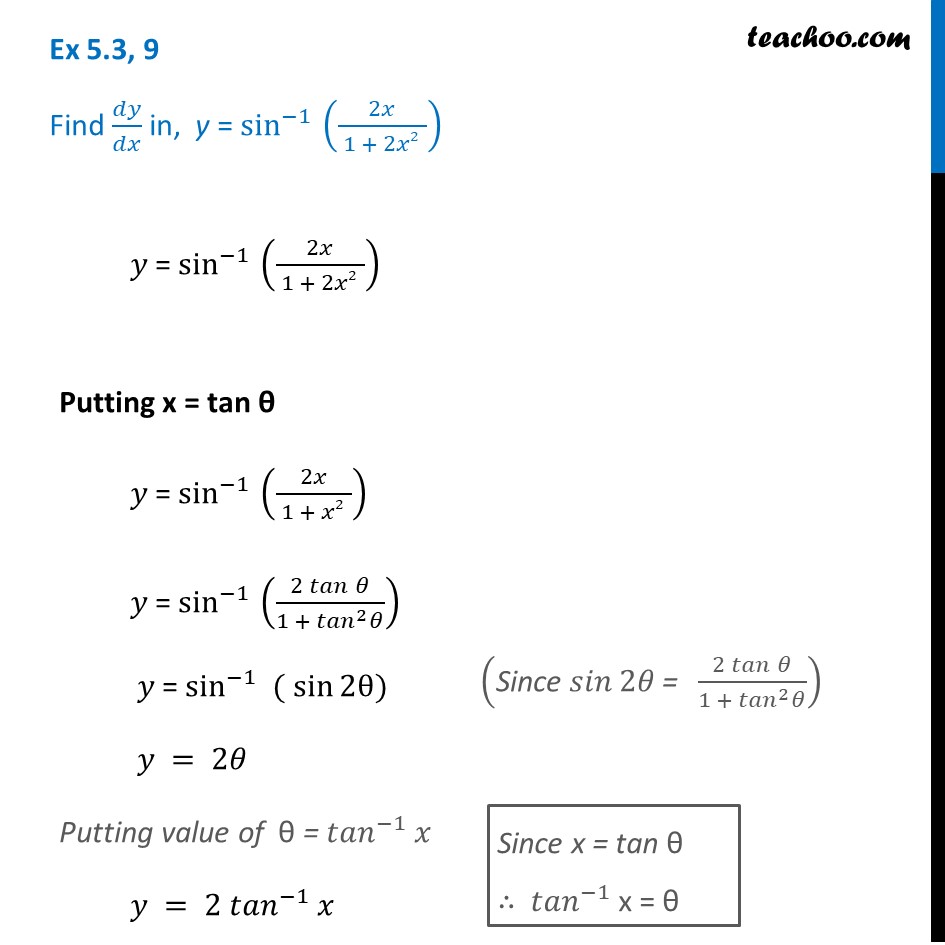



Ex 5 3 9 Find Dy Dx In Y Sin 1 2x 1 2x2 Chapter 5




Ex 9 4 9 Find General Solution Dy Dx Sin 1 X Chapter 9




If Y Sin 1 Cos X Cos 1 Sin X Prove That Dydx 2




If Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Then Dy Dx Is Equal To




Example 41 If Y Sin 1 X Show That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 X Dy Dx 0




Find Dy Dx In The Following Y Sin 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 0 Lt X Lt 1
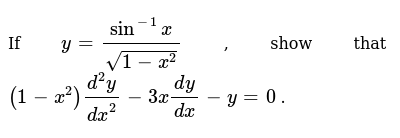



If Y Sin 1 X Sqrt 1 X 2 Show That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 3x Dy Dx Y 0
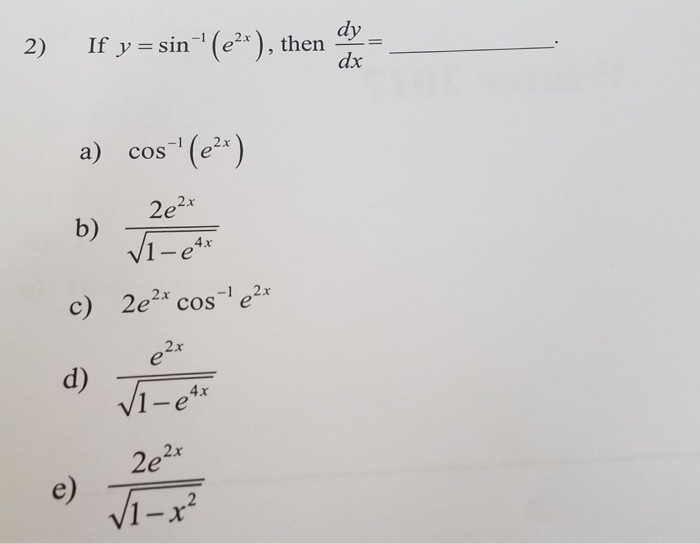



Solved If Y Sin 1 E 2x Then Dy Dx A Chegg Com
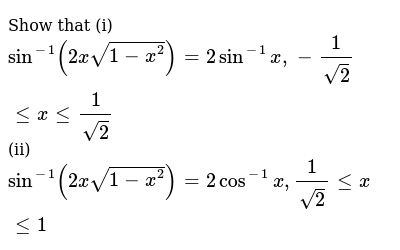



Show That I Sin 1 2xsqrt 1 X 2 2sin 1 X 1 Sqrt 2 Lt Xlt 1 Sqrt 2 Ii Sin 1 2xsqrt 1 X 2 2cos 1 X 1 Sqrt 2 Lt Xlt 1
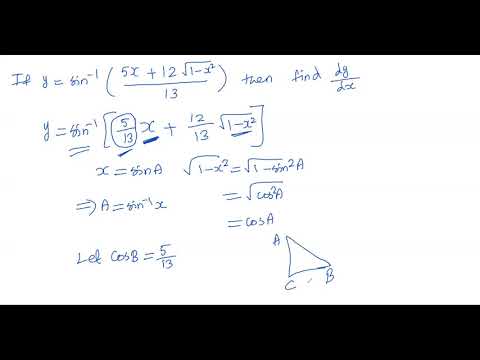



If Y Sin 1 5x 12 Square Root 1 X 2 13 Then Find Dy Dx Youtube




If Y Sin 1x 2 Then Show That 1 X 2 D 2ydx 2 X Dydx 2



If Y F 2x 1 X 2 1 And F X Sin 2 X Then Dy Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




How Do You Find Dy Dx For Y 2x Sqrt X 1 Socratic



Sin 2x X 2 Integral Musillar
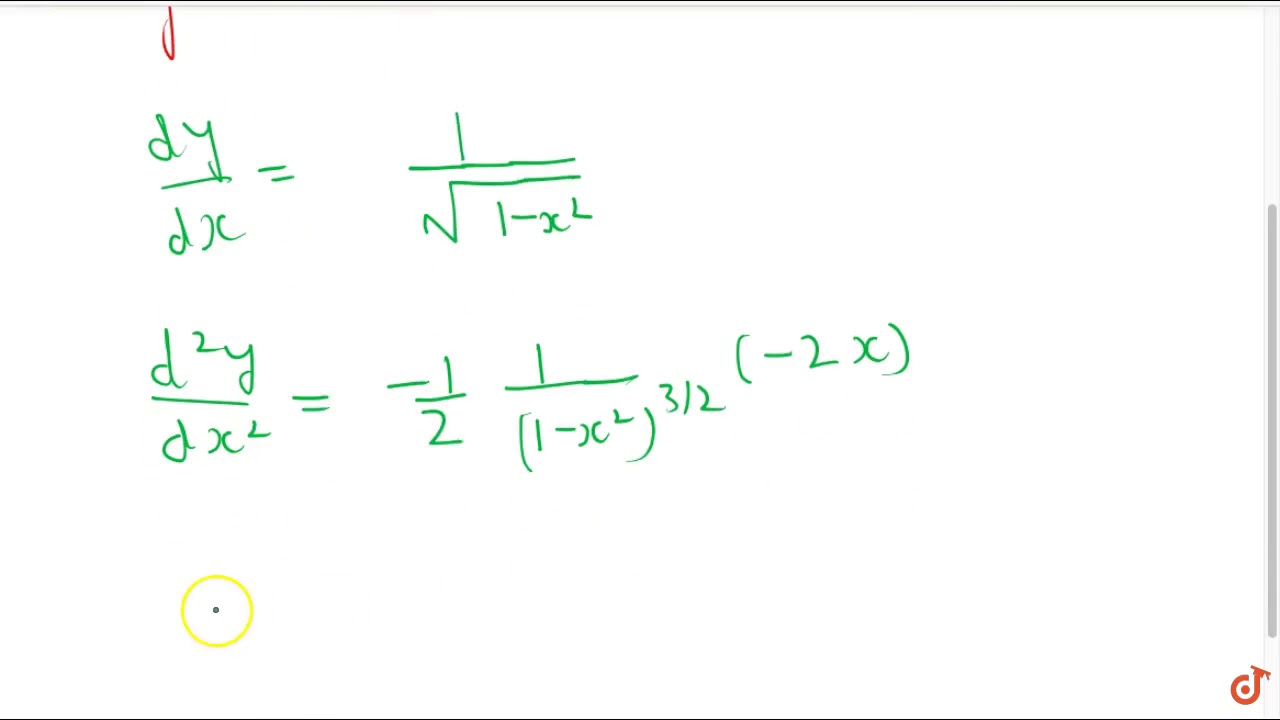



If Y Sin 1 X Then Show That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx 0 Youtube




Find Dy Dx Of Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 1 2 Less Than X Less Than 1 2 Youtube



3




Find Dx Dy For Y Cos 1 2x 1 X 2 1 X 1 Mathematics Shaalaa Com
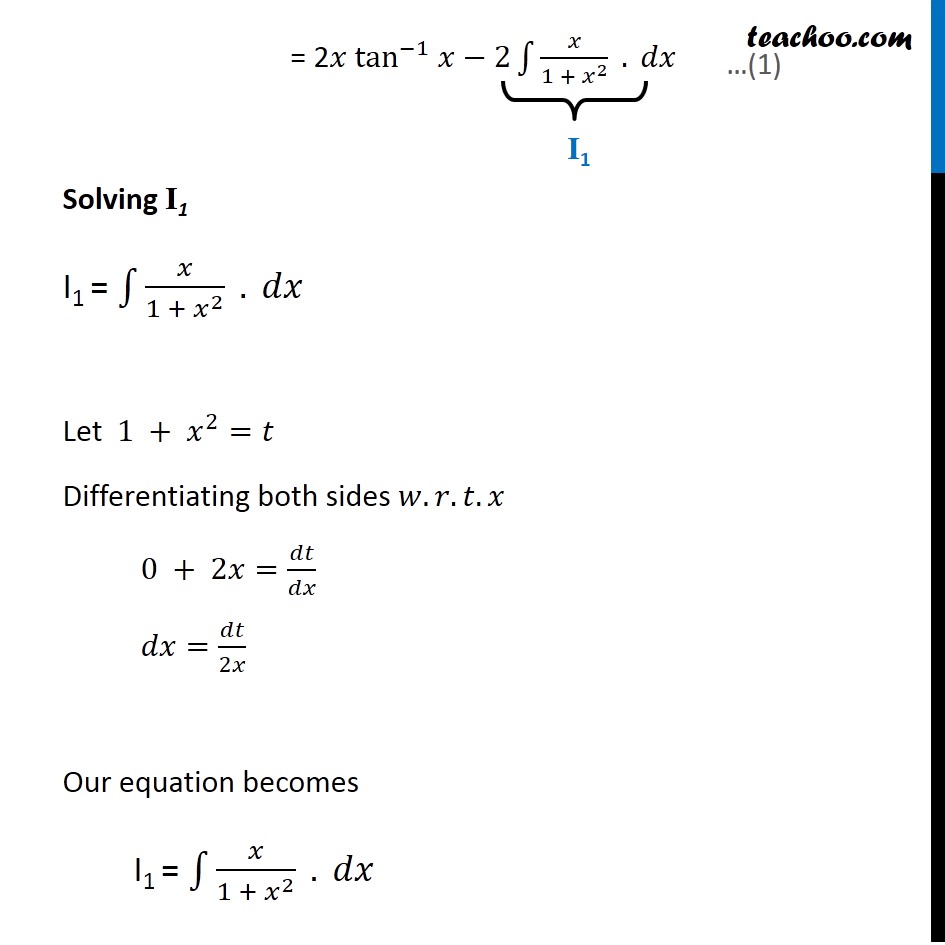



Ex 7 6 22 Integrate Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Teachoo Ex 7 6




Ex 5 3 13 Find Dy Dx In Y Cos 1 2x 1 X2 Ncert Ex 5 3




Misc 13 Find Dy Dx If Y Sin 1 X Sin 1 Root 1 X2 Miscellaneous




Solved Dy Dx For The Following Fourteen Problems Find Chegg Com



Find Dy Dx Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 1 2 X 1 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



How To Integrate Sin Y 1 Cos Y Dy Quora




Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Formula Baldwin Cyprian



If Y Cos 1 2x 3 1 X 2 13 Then Find Dy Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Solved Find The Derivative For The Following Functions Find Chegg Com



Solve The Linear Differential Equation Dy Dx Sin 2 X 1 X 3 3x 2 1 X 3 Y Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



How To Find Derivative Of Y Sin 2x 1 X 2 Quora




Differentiate Sin 1 2x 1 1 4x Wrt X Mathematics Topperlearning Com P8672lhh
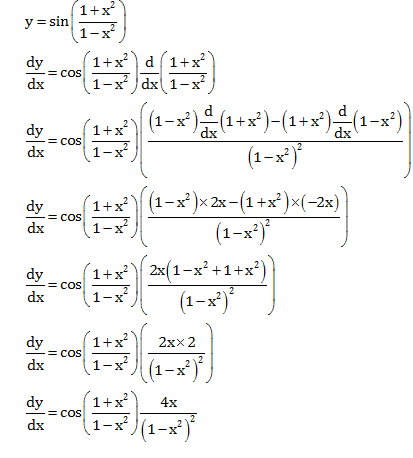



Find Dy Dx Y Sin 1 X2 1 X2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 8s1l799




If Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Then Find Dy Dx Youtube



If Y Logcos X Sinx Logsin X Cos X 1 Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Then Prove That Dy Dx At X P 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Differentiate Tan 1 X 1 X 2 With Respect To Sin 1 2x 1 X 2
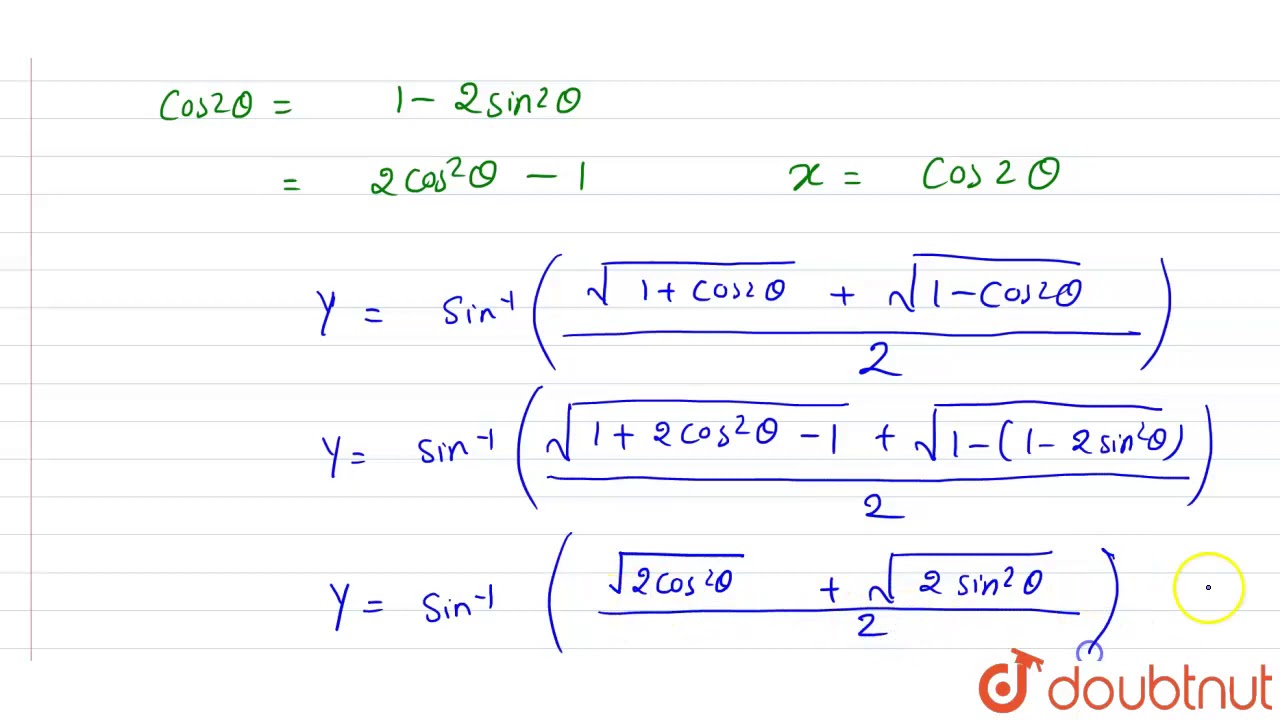



Y Sin 1 Sqrt 1 X Sqrt 1 X 2 Then Dy Dx Youtube




Differentiate Sin 1 2x 1 3x 1 36 X Wrt X Mathematics Topperlearning Com Gnbp3ull




Ex 5 4 2 Differentiate E Sin 1 X Teachoo Ex 5 4



Find Dy Dx Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Solved 3 Find Dy Y Sin 7x2 5 A 14x Sin 7x2 5 B Chegg Com




Differentiate Sin 1 2 X 13 X1 36 X With Respect To X




Ex 5 3 12 Find Dy Dx In Y Sin 1 1 X2 1 X2 Chapter 5




Solved Find Dy Dx In Y Sin 231 22 I E Y Arcsin 2x V1 Chegg Com
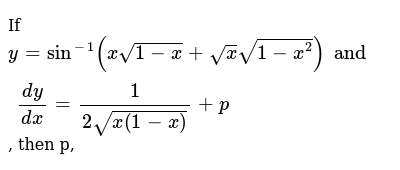



If Y Sin 1 X Sqrt 1 X Sqrtx Sqrt 1 X 2 And Dy Dx 1 2 Sqrt X 1 X P Then P




Ex 5 3 15 Find Dy Dx In Y Sec 1 1 2x2 1 Chapter 5




Diferentiate Wrt X If Y Sin 2 Tan 1 1 X 1 X 1 2 Show That Dy Dx X 1 X2 1 2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 6g8c5y




Find Dy Dx For Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Find Dy Dx X Cos 1 1 1 T2 1 2 Y Sin 1 T 1 T2 1 2 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com 6ebbrcqq



If Y Sin 1 X 2 Then Prove That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx 2 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Sin M Sin 1 X What Is The Value Of D 2 Y Dx 2 At X 0 Youtube




Solved Use Implicit Differentiation To Find Dy Dx In Chegg Com



How To Differentiate Sin X 2 1 Using First Principle Quora




Ex 5 3 2 Find Dy Dx In 2x 3y Sin Y Class 12 Ncert



If Y Sin 1x 2 Cos 1x 2 Then Prove That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿