
If Y Cos 1 2x 3 1 X 13 Find Dy Dx Brainly In
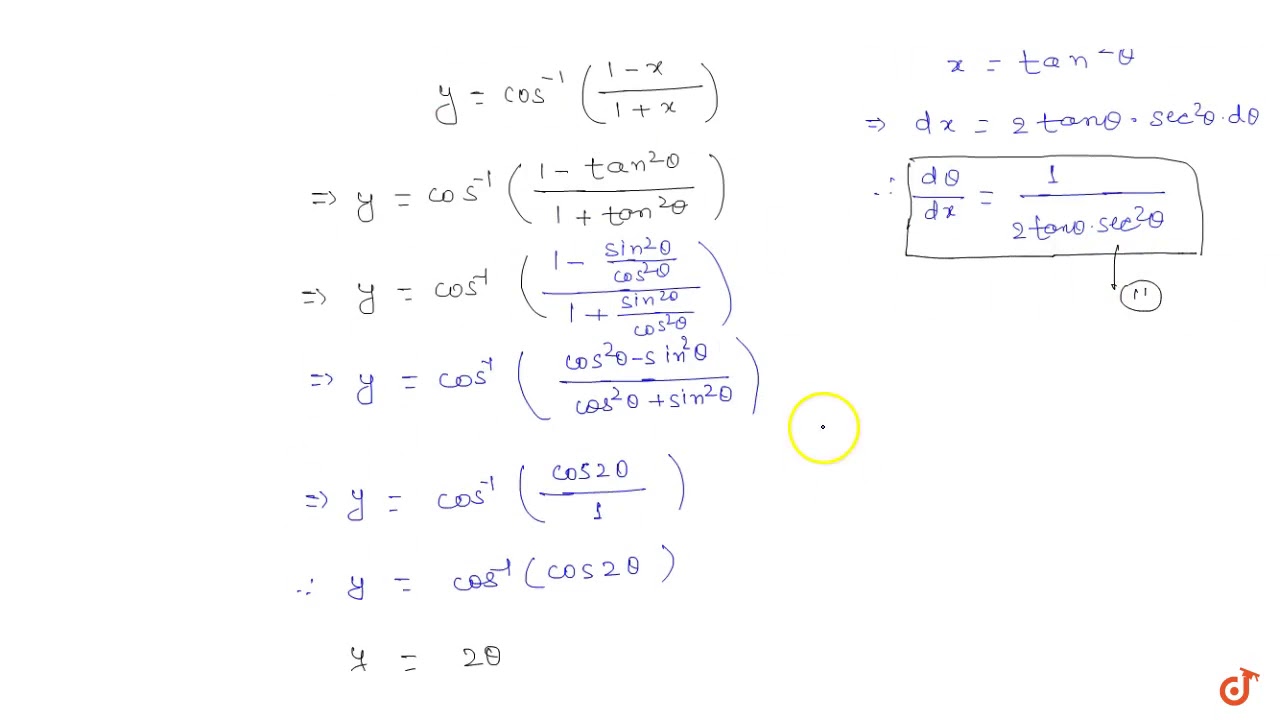
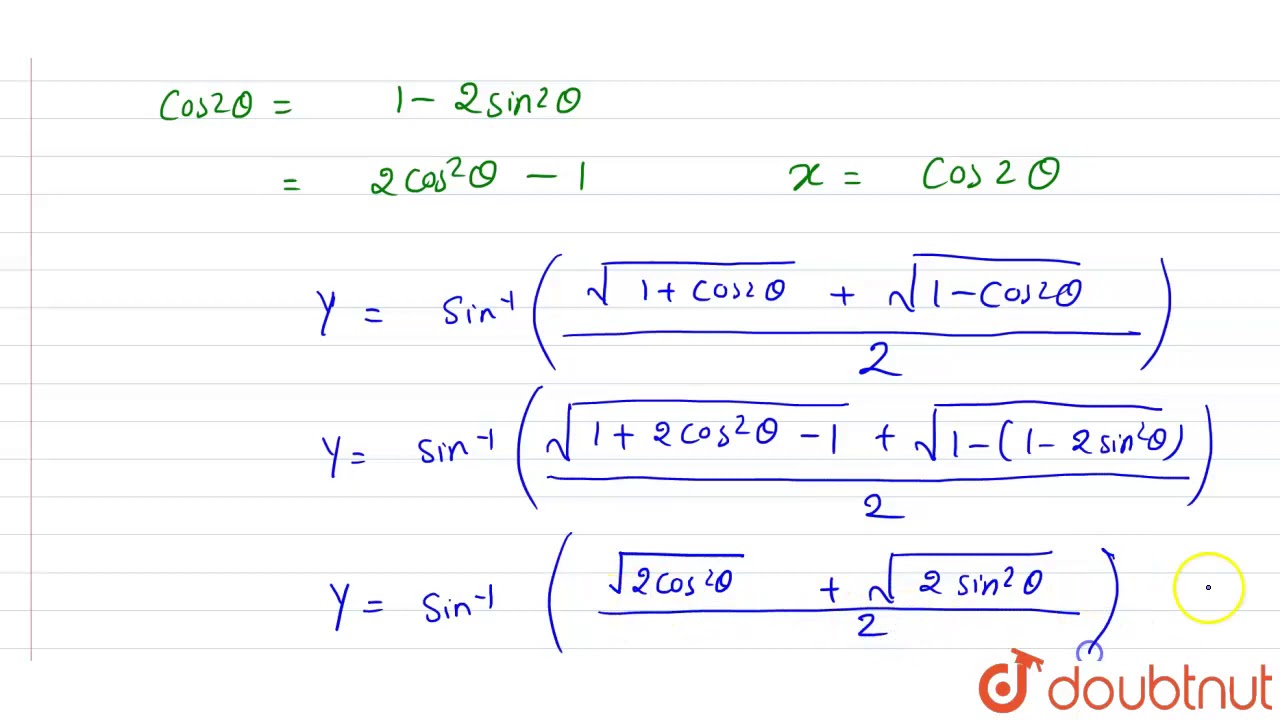
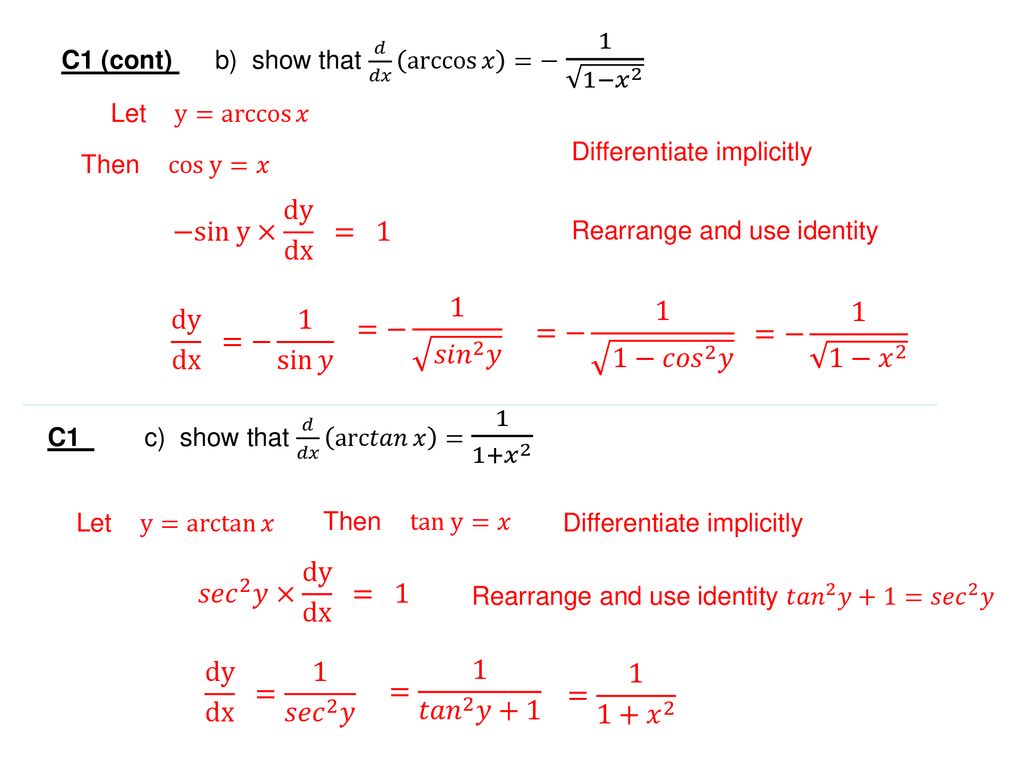
\frac{dy}{dx}=1x^2y^2, Given Here, \frac{dy}{dx} represents the derivative of y with respect to x I will solve for x and y, treating y as a function of x (essentially y=f(x)) \int \frac{dy}{dx}dx=\int 1x^2y^2dx Transcript Ex 53, 15 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 in, y = sec–1 (1/( 2𝑥2−1 )), 0 < x < 1/√2 y = sec–1 (1/( 2𝑥^2 − 1 )) 𝒔𝒆𝒄𝒚 = 1/(2𝑥^2 − 1) 𝟏/𝐜𝐨𝐬𝒚 = 1/(2𝑥^2 − 1) cos𝑦 = 2𝑥2−1 y = cos –1 (2𝑥2−1) Putting 𝑥 = cosθ 𝑦 = cos –1 (2𝑐𝑜𝑠2𝜃−1) 𝑦 = cos –1 (cos2 𝜃) 𝑦 = 2𝜃 Putting value of θ
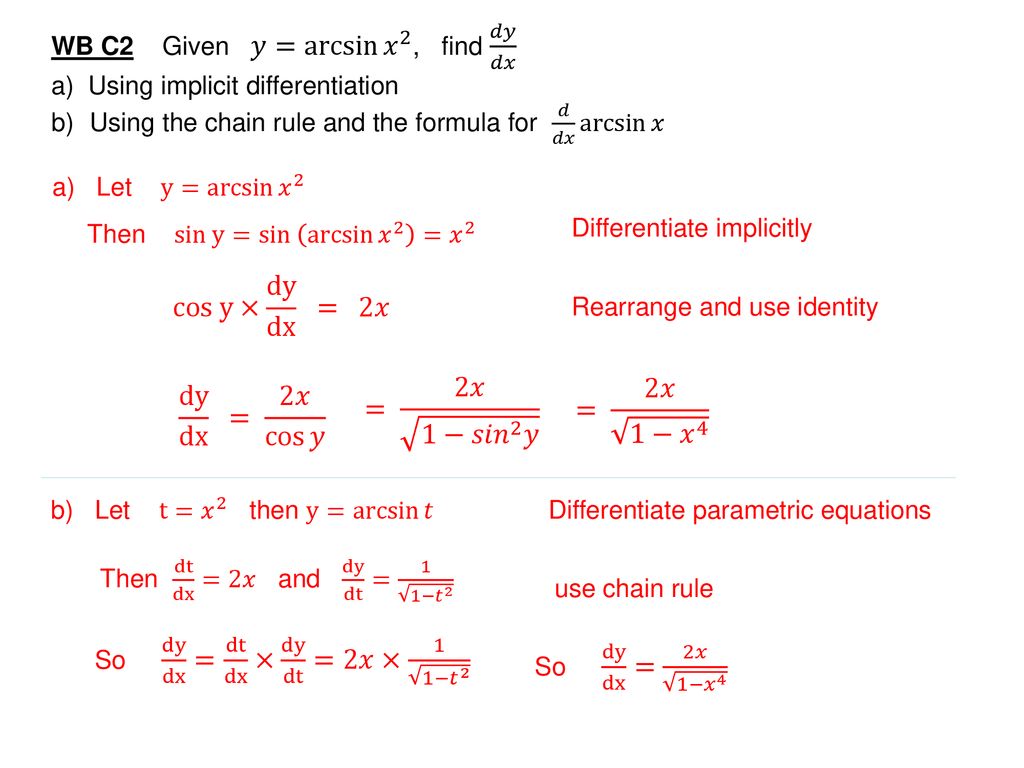
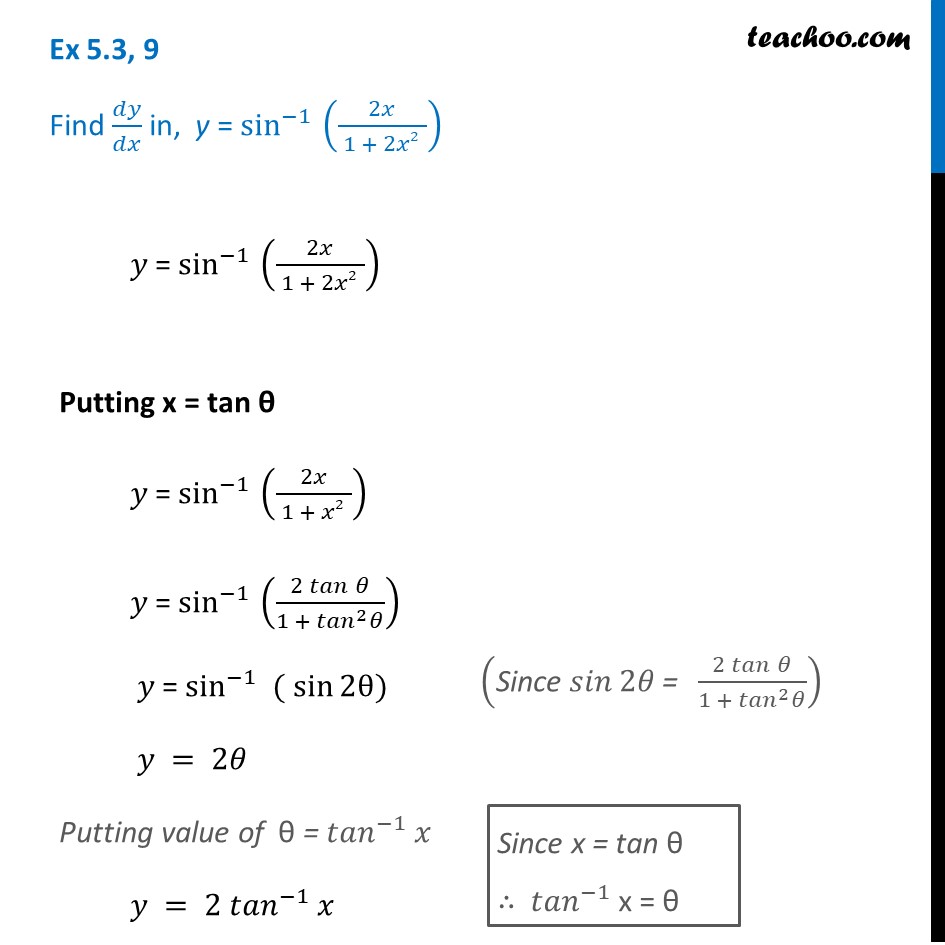
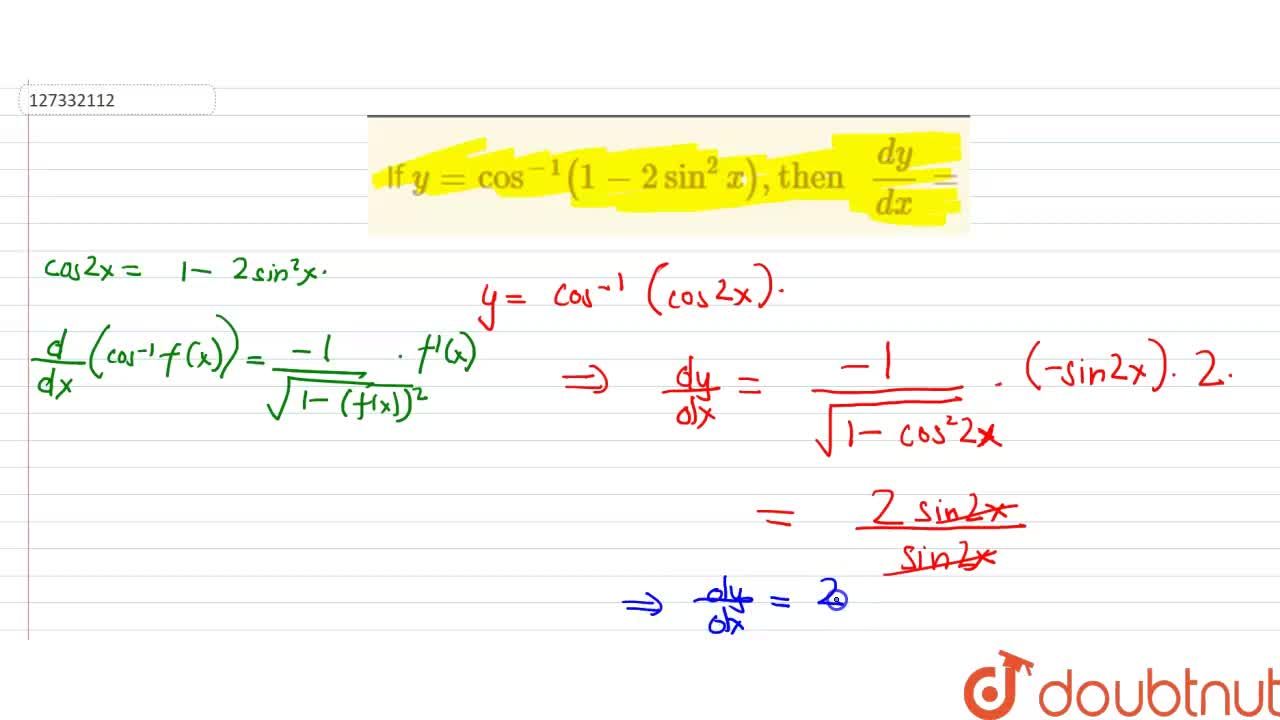
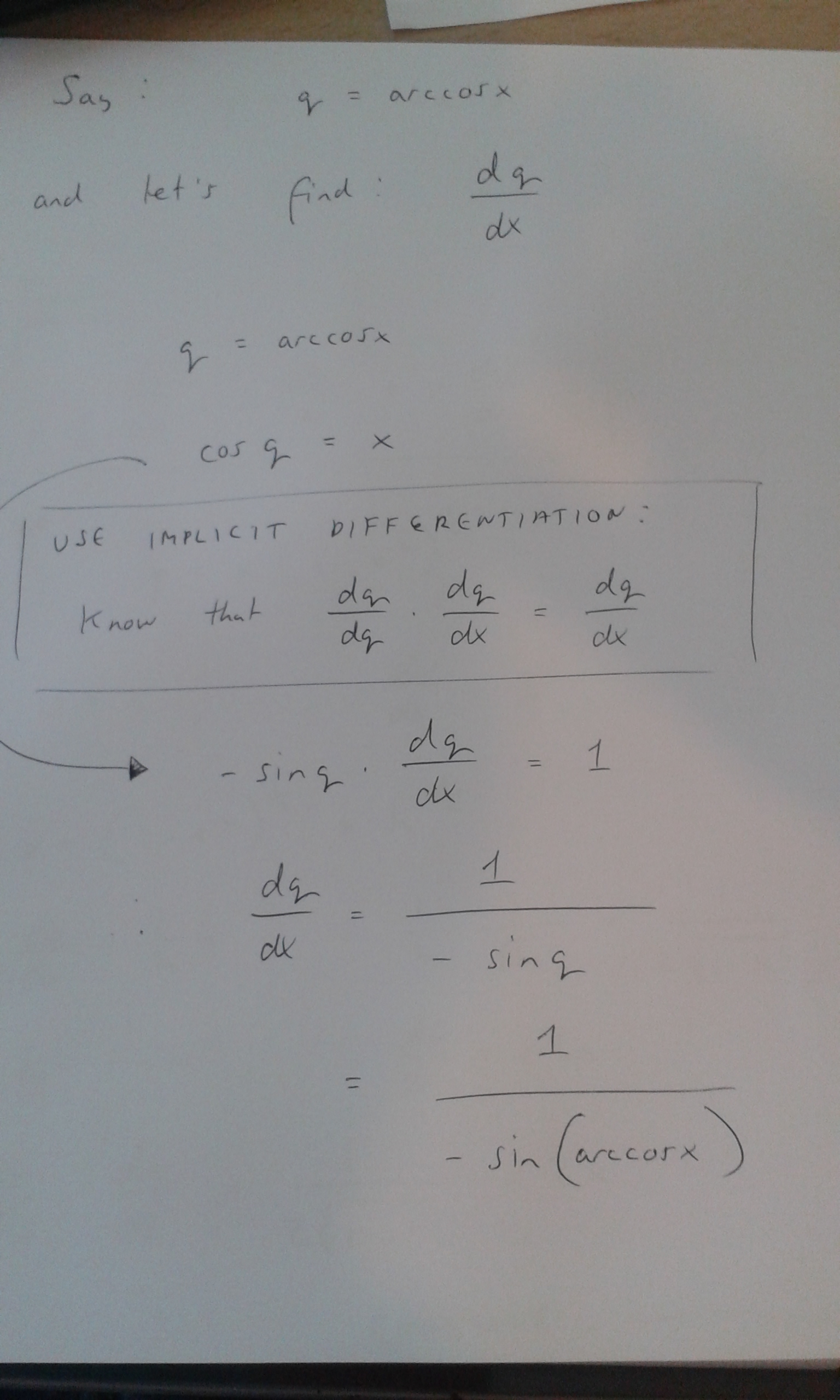
Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx
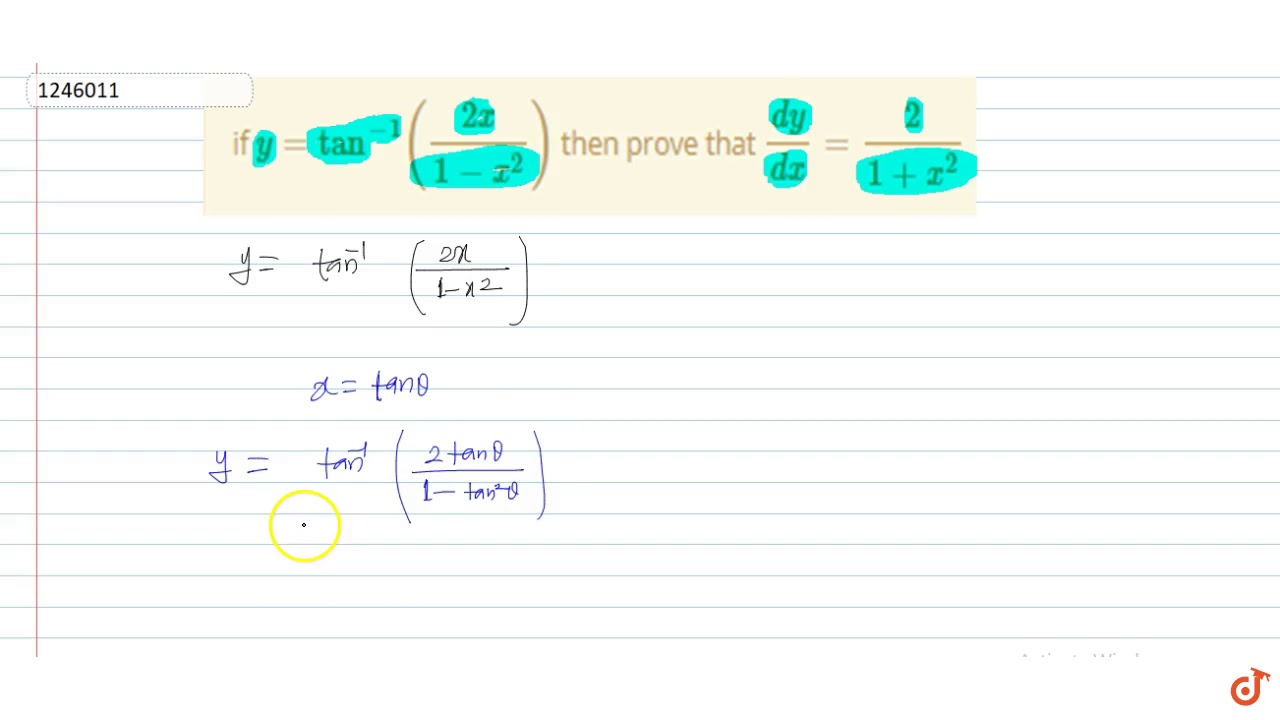
Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx- Ex 57, 12 Chapter 5 Class 12 Continuity and Differentiability (Term 1) Last updated at by Teachoo Next Ex 57, 13 Important → Chapter 5 Class 12 Continuity and Differentiability (Term 1) Serial order wise; Explanation Here , (1)x1 2 y1 2 = a1 2 Diff wrt x ,we get 1 2 x1 2 −1 1 2 y1 2−1 ⋅ dy dx = 0 ⇒ x− 1 2 y− 1 2 dy dx = 0 ⇒ y− 1 2 dy dx = −x− 1
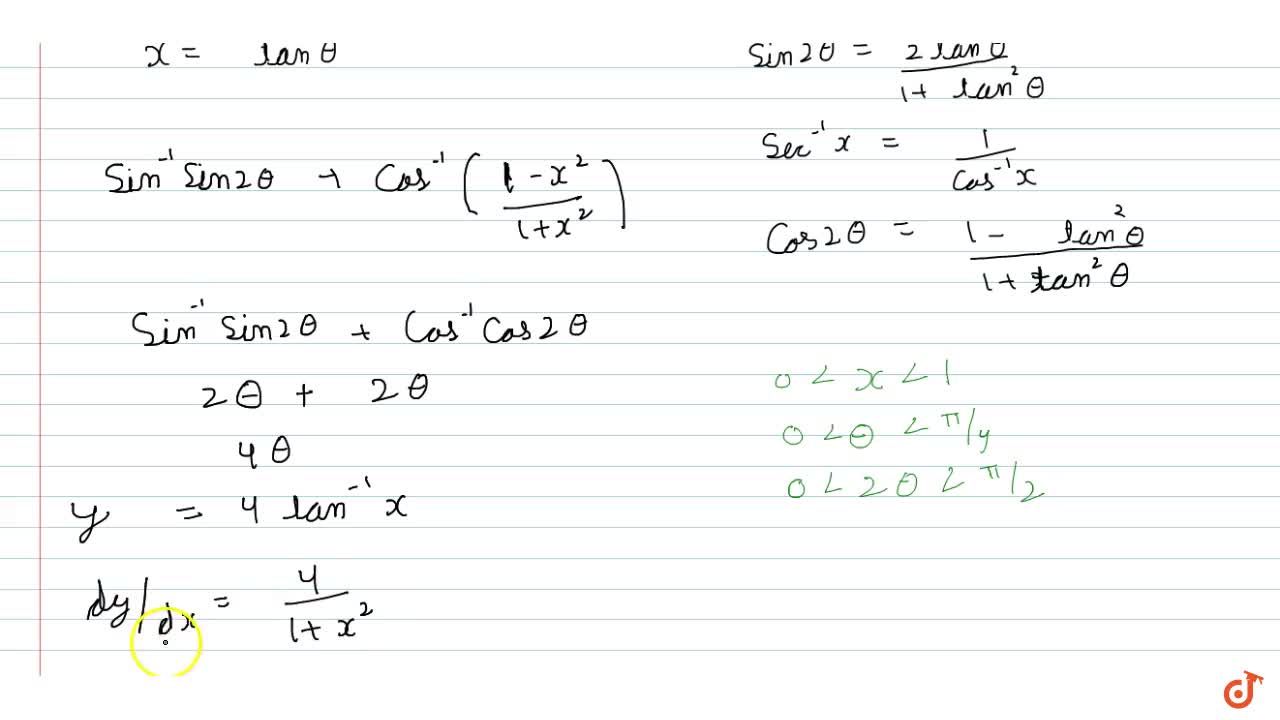
If Y Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 0ltxlt1 Prove That Dy Dx 4 1 X 2 B X 1
Example 19 Find the general solution of the differential equation 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥−𝑦=cos𝑥 Differential equation is of the form 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥𝑃𝑦=𝑄 where P = −1 & Q = cos x IF = e^∫1 𝑝𝑑𝑥 IF = e^(−∫1 1𝑑𝑥) IF = 𝑒^(−𝑥) Solution is y(IF) = ∫1 〖(𝑄×𝐼𝐹) 𝑑𝑥𝑐〗 𝑦𝑒^(−𝑥) = ∫1 𝑒^(−𝑥) cos〖𝑥𝑐〗 LetIf y = 25^(log5 sin x ) 16^(log4cos x ) " then " (dy)/(dx) = Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams2) Find and of the following equation then simplify whenever possible dx² x = Cos ß Sin ß y = Sin ß – Cos ß Question Transcribed Image Text 2) Find and d²y of the following equation then simplify whenever possible dx dx² x = Cos B Sin B у 3DSin B — Cos B
y=(x1)sin2xcos^3(2x1)的导数 主要内容: 本文通过三角函数的导数公式以及函数乘积、函数和差的求导法则,介绍函数y=(2x1)sin2xcos^4(2x1)的一阶、二阶和三阶导数的计算步骤。 一阶导数计算: ∵y=(x1)sin2xcos^3(2x1) ∴dy/dxIf y=cos^1(2xsqrt(1x^2)), find dy/dx Maharashtra State Board HSC Science (Electronics) 12th Board Exam Question Papers 185 Textbook Solutions MCQ Online Tests 60 Important Solutions 3796 Question Bank Solutions 124 Concept Notes & Ex 53, 11 Chapter 5 Class 12 Continuity and Differentiability (Term 1) Last updated at by Teachoo Next Ex 53, 12 Important → Chapter 5 Class 12 Continuity and Differentiability (Term 1) Serial order wise;
Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dxのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | 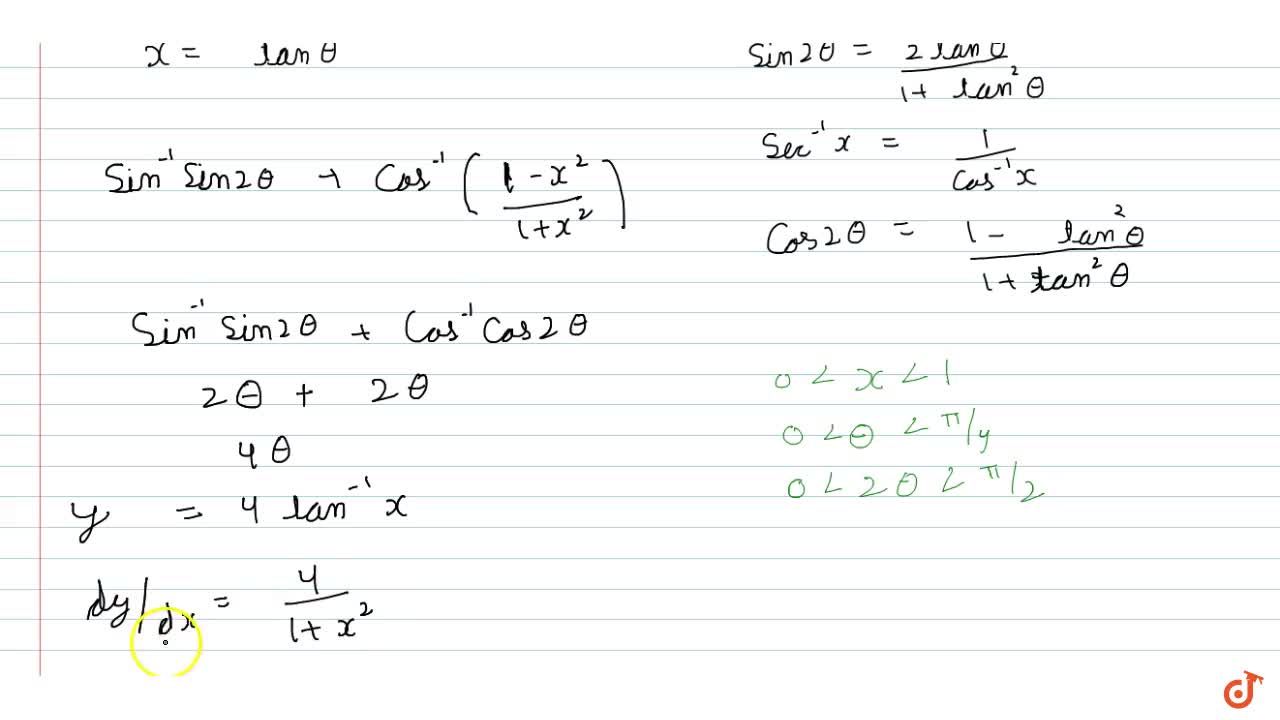 | |
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
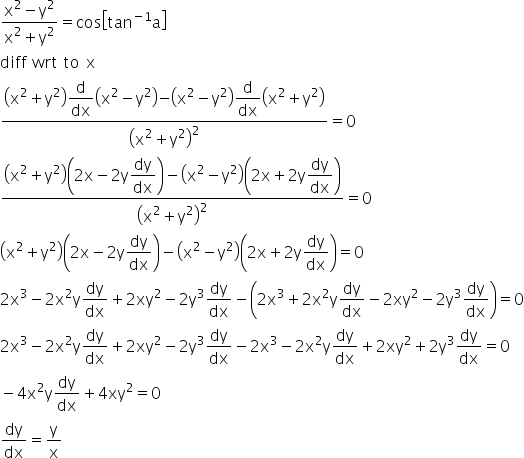 |  | |
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
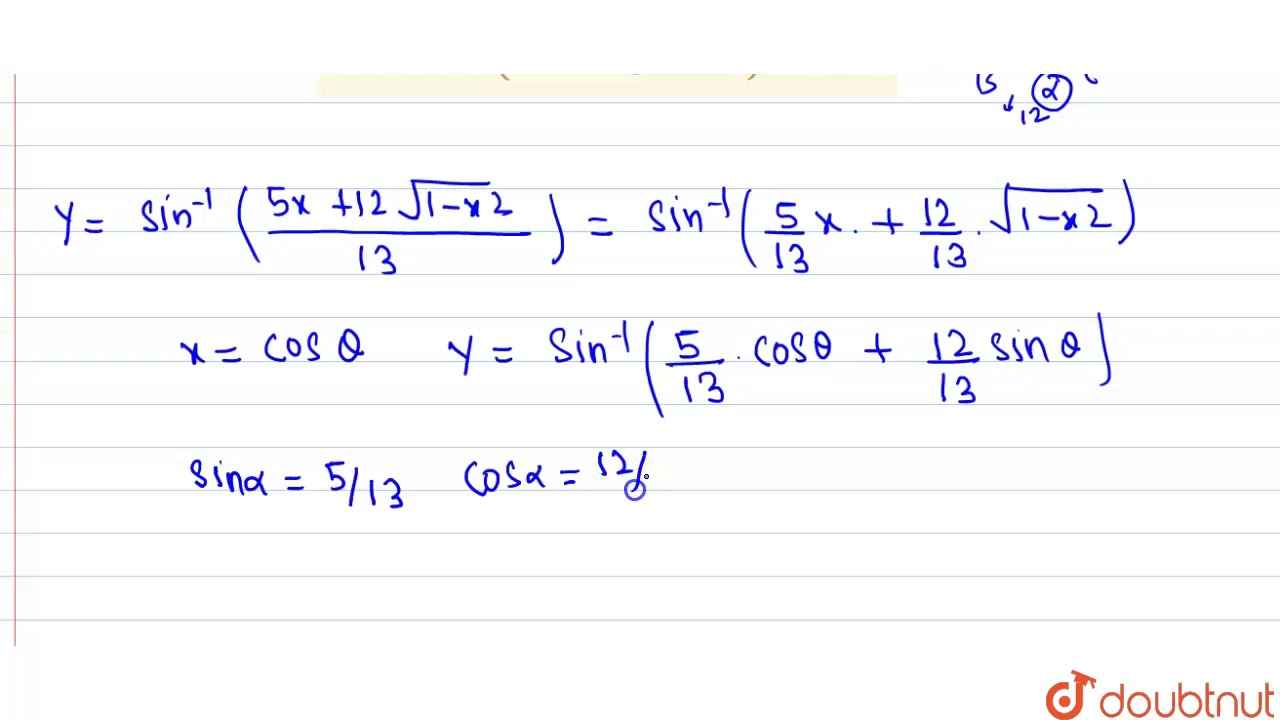 |  |  |
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
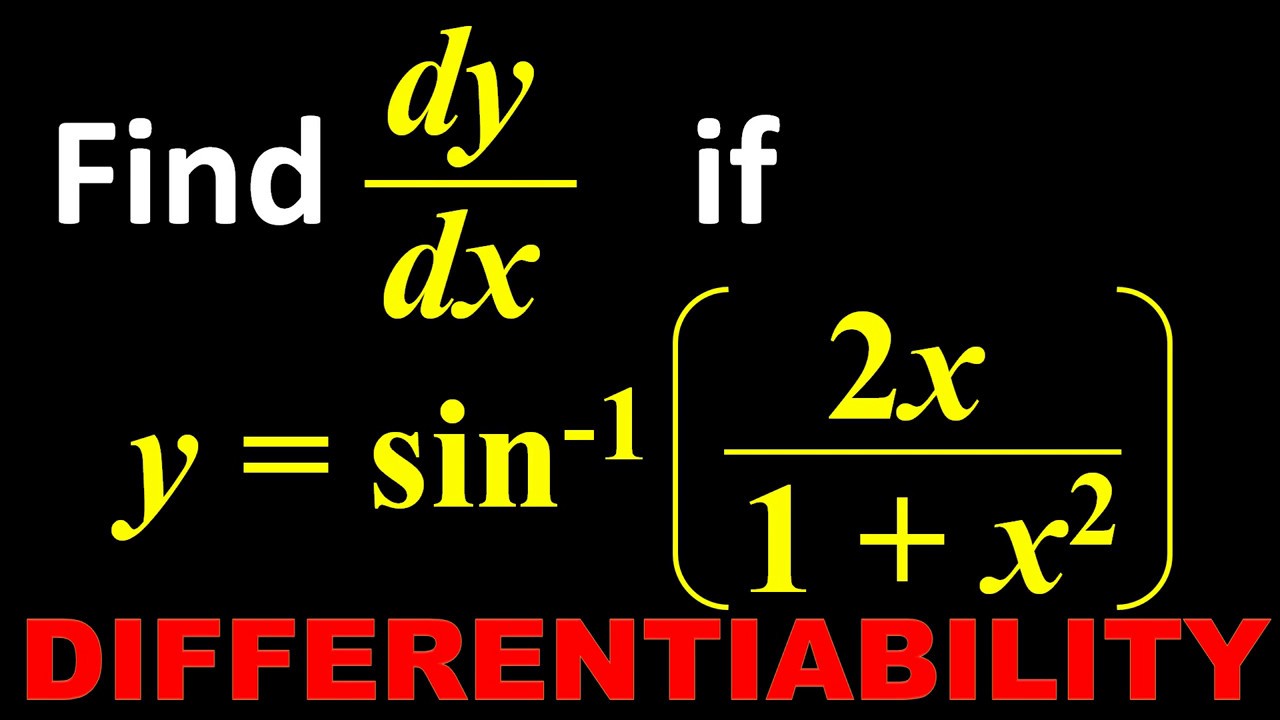 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | ||
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 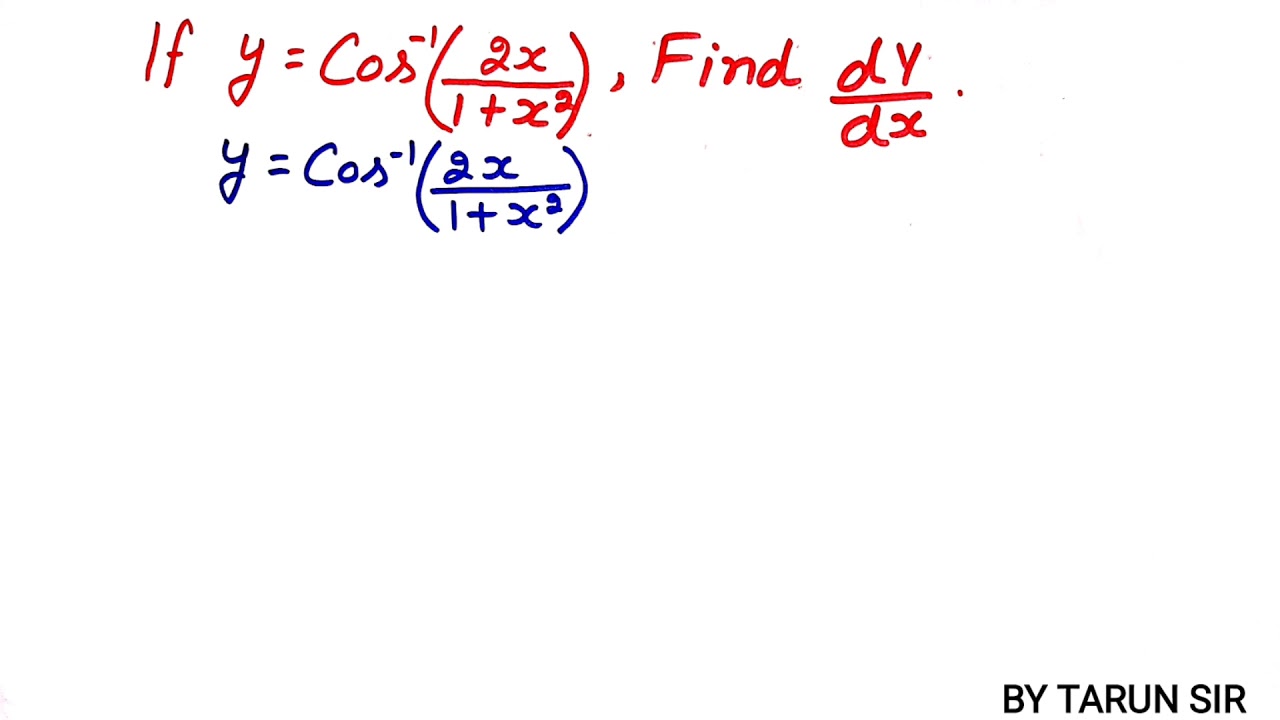 |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 | ||
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |
Y = x 2 (cos (x)) therefore we will need to use the product rule, dy/dx = u dv/dx v du/dx where u = x 2 and v = cos (x) du/dx = 2x and dv/dx = sin (x), (don't forget the negative symbol when differentiating cosine) dy/dx = x 2 ( sin (x)) cos (x) (2x) dy/dx = 2x (cos (x)) x 2 (sin (x)) Answered by Joseff S • Maths tutorFree implicit derivative calculator implicit differentiation solver stepbystep
Incoming Term: y=cos^-1(2x/1+x^2) then dy/dx,




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿